




| Faculty / Departement ⤶ |
Register by Units | Register by Projects | Register of researchers |
| Register by Collaborations | Ranking by Domains | Ranking by Frascati | Disciplines CREF |
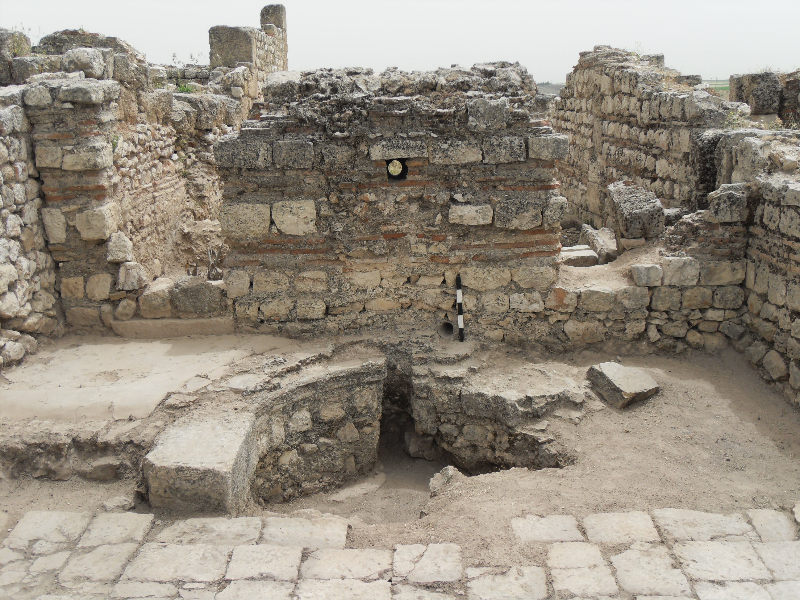
Analysis of ancient hydraulic systems
Units : TIPs - Transport phenomena and process engineering | ULB828
Description :
For several years, we have developed a collaboration with archaeologists in order to analyze ancient hydraulic systems. It is commonly accepted that the Romans possessed a technical mastery of water supply. Nevertheless, few writings on this engineering practice are available. Moreover, due to the scientific knowledge in the field of fluid mechanics during the Roman period, these writings do not contain the usual modern information on the characterization of a hydraulic system. However, thanks to the current knowledge in fluid mechanics, it is now possible to simulate the flow that was taking place in a hydraulic remains presenting a good state of conservation. It is therefore possible to supplement the usual field information with data such as flow rates, velocity and pressure fields, energy losses, yields... In recent years, we were interested in fountains found in large houses in the southern part of the ancient Roman city of Apamea (Byzantine times). We were able to characterize their functioning using classical fluid mechanics approaches. The analysis of the results obtained clearly shows that these fountains were supplied with water by an aqueduct and that this feed was technically feasible in view of the remains of the Byzantine aqueduct still present in the north of the city. We were also interested in a peculiar system that can be observed within the ruins of the city of Perge (Turkey). During the Roman Imperial Period, at the middle of the main street of the city, a water channel was operated. This channel has peculiar dimensions and blocks were positioned inside it at a regular interval. By using open surface flow theory, we have been able to characterize the flow in this system and in diversions originating from it. Selected publications : Vekemans, O., & Haut, B. Hydraulic analysis of the water supply system of the Roman city of Perge. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 16, 322-329. 2017 Haut, B., Zheng, X.Y., Mays, L., Han, M., Passchier, C., & Angelakis, A.N. Evolution of rainwater harvesting in urban areas through the millennia. A sustainable technology for increasing water availability. In W.J.H. Willems & H.P.J. van Schaik (Eds.), Water and Heritage. The Netherlands: Sidestone Press. 2015 Vannesse, M., Haut, B., Debaste, F., & Viviers, D. Analysis of three private hydraulic systems operated in Apamea during the Byzantine period. Journal of Archaeological Science, 46, 245-254. 2014
Web site: https://tips-ulb.be/research-topics/ancient-hydraulic-systems
List of persons in charge :

×![]()


